Overview
![Achilles Tendonitis]() You?re a prime
candidate for acquiring Achilles Tendonitis if you?re a runner or some other kind of athlete requiring heavy use of your calves and their attached tendons. Then again, -anybody- can get tendonitis of
the Achilles tendons. All for very predictable reasons. Perhaps you have Achilles Tendon pain from cycling. Or standing at work. Or walking around a lot. Anything we do on our feet uses our lower leg
structures, and the Achilles tendon bears LOTS of torque, force, load, etc. The physical dynamic called Tendonitis can show up anywhere. On the Achilles Tendon is as good a place as any. Repetitive
strain injury can show up anywhere in the body that there is repetitive strain. It's an obvious statement, but worth paying attention to.
You?re a prime
candidate for acquiring Achilles Tendonitis if you?re a runner or some other kind of athlete requiring heavy use of your calves and their attached tendons. Then again, -anybody- can get tendonitis of
the Achilles tendons. All for very predictable reasons. Perhaps you have Achilles Tendon pain from cycling. Or standing at work. Or walking around a lot. Anything we do on our feet uses our lower leg
structures, and the Achilles tendon bears LOTS of torque, force, load, etc. The physical dynamic called Tendonitis can show up anywhere. On the Achilles Tendon is as good a place as any. Repetitive
strain injury can show up anywhere in the body that there is repetitive strain. It's an obvious statement, but worth paying attention to.
Causes
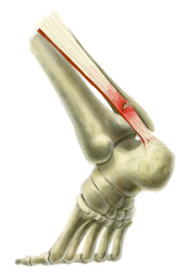
The Achilles tendon is a strong band of connective tissue that attaches the calf muscle to the heel bone. When the muscle contracts, the tendon transmits the power of this contraction to the heel, producing movement. The Achilles tendon moves through a protective sheath and is made up of thousands of tiny fibres. It is thought that Achilles tendonitis develops when overuse of the tendon causes the tiny fibres that make up the tendon to tear. This causes inflammation, pain and swelling. As the tendon swells it can begin to rub against the sheath surrounding it, irritating the sheath and causing it too to become inflamed and swollen. It has a poor blood supply, which can make it susceptible to injury and can make recovery from injury slow. Factors that can lead to the development of Achilles tendonitis include, tight or weak calf muscles, rapidly increasing the amount or intensity of exercise. Hill climbing or stair climbing exercises. Changes in footwear, particularly changing from wearing high-heeled shoes to wearing flat shoes. Wearing inadequate or inappropriate shoes for the sporting activity being undertaken. Not adequately warming up and stretching prior to exercise. A sudden sharp movement that causes the calf muscles to contract and the stress on the Achilles tendon to be increased. This can cause the tendon fibres to tear.
Symptoms
The Achilles tendon is a strong muscle and is not usually damaged by one specific injury. Tendinitis develops from repetitive stress, sudden increase or intensity of exercise activity, tight calf muscles, or a bone spur that rubs against the tendon. Common signs and symptoms of Achilles Tendinitis include, gradual onset of pain at the back of the ankle which may develop in several days up to several months to become bothersome. Heel pain during physical activities which may diminish after warming up in early stages, or become a constant problem if the problem becomes chronic. Stiffness at the back of the ankle in the morning. During inactivity, pain eases. Swelling or thickening of the Achilles tendon. Painful sensation if the Achilles tendon is palpated. If a pop is heard suddenly, then there is an increased chance that the Achilles tendon has been torn and immediate medical attention is needed.
Diagnosis
To diagnose the condition correctly, your doctor will ask you a few questions about the pain and swelling in your heel. You may be asked to stand on the balls of your feet while your doctor observes your range of motion and flexibility. The doctor may also touch the area directly. This allows him to pinpoint where the pain and swelling is most severe.
Nonsurgical Treatment
The aim, when treating Achilles tendinitis, is to relieve pain and reduce swelling. The kind of treatment used can vary, based on the severity of the condition and whether or not the patient is a professional athlete. After diagnosis, the doctor will decide which method of treatment is required for the patient to undergo, it is likely that they will suggest a combination. Stretching achilles tendon, a doctor might show the patient some stretching exercises that help the Achilles tendon heal, as well as preventing future injury. Methods used to treat Achilles tendinitis include, ice packs - applying these to the tendon, when in pain or after exercising, can alleviate the pain and inflammation. Resting, this gives the tissue time to heal. The type of rest needed depends on the severity of the symptoms. In mild cases of Achilles tendinitis, it may mean just reducing the intensity of a workout, in severe cases it might mean complete rest for days or weeks. Elevating the foot, swelling can be reduced if the foot is kept raised above the level of the heart. Exercise and stretching, a doctor might show the patient some stretching exercises that help the Achilles tendon heal, as well as preventing future injury. They may, instead, refer the patient to a physiotherapist or another specialist. The exercises learned will improve the flexibility of the area and likely increase calf strength. Pain relievers - non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS), such as ibuprofen can reduce pain and swelling. If you suffer from asthma, kidney disease or liver disease do not take NSAIDs without first checking with your doctor. Steroid injections, these can reduce tendon swelling, but should be performed with caution, as this process has been associated with a greater risk of tendon rupture. A doctor would likely perform the injection while scanning the area with ultrasound to reduce this risk. Compression bandages and orthotic devices, such as ankle supports and shoe inserts can aid recovery as they take the stress off the Achilles tendon.
![Achilles Tendonitis]()
Surgical Treatment
Most people will improve with simple measures or physiotherapy. A small number continue to have major problems which interfere with their lifestyle. In this situation an operation may be considered. If an operation is being considered, the surgeon will interview you and examine you again and may want you to have further treatment before making a decision about an operation. Before undergoing Achilles tendonitis surgery, London based patients, and those who can travel, will be advised to undergo a scan, which will reveal whether there is a problem in the tendon which can be corrected by surgery. Patients will also have the opportunity to ask any questions and raise any concerns that they may have, so that they can proceed with the treatment with peace of mind.
Prevention
The following measures can significantly reduce the risk of developing Achilles tendonitis. Adequately stretch and warm up prior to exercise. Warm down and stretch after exercise. Choose footwear carefully and use footwear appropriate to the sport being undertaken. Use orthotic devices in footwear to correctly support the foot. Exercise within fitness levels and follow a sensible exercise programme. Develop strong, flexible calf muscles.
 You?re a prime
candidate for acquiring Achilles Tendonitis if you?re a runner or some other kind of athlete requiring heavy use of your calves and their attached tendons. Then again, -anybody- can get tendonitis of
the Achilles tendons. All for very predictable reasons. Perhaps you have Achilles Tendon pain from cycling. Or standing at work. Or walking around a lot. Anything we do on our feet uses our lower leg
structures, and the Achilles tendon bears LOTS of torque, force, load, etc. The physical dynamic called Tendonitis can show up anywhere. On the Achilles Tendon is as good a place as any. Repetitive
strain injury can show up anywhere in the body that there is repetitive strain. It's an obvious statement, but worth paying attention to.
You?re a prime
candidate for acquiring Achilles Tendonitis if you?re a runner or some other kind of athlete requiring heavy use of your calves and their attached tendons. Then again, -anybody- can get tendonitis of
the Achilles tendons. All for very predictable reasons. Perhaps you have Achilles Tendon pain from cycling. Or standing at work. Or walking around a lot. Anything we do on our feet uses our lower leg
structures, and the Achilles tendon bears LOTS of torque, force, load, etc. The physical dynamic called Tendonitis can show up anywhere. On the Achilles Tendon is as good a place as any. Repetitive
strain injury can show up anywhere in the body that there is repetitive strain. It's an obvious statement, but worth paying attention to.Causes
The Achilles tendon is a strong band of connective tissue that attaches the calf muscle to the heel bone. When the muscle contracts, the tendon transmits the power of this contraction to the heel, producing movement. The Achilles tendon moves through a protective sheath and is made up of thousands of tiny fibres. It is thought that Achilles tendonitis develops when overuse of the tendon causes the tiny fibres that make up the tendon to tear. This causes inflammation, pain and swelling. As the tendon swells it can begin to rub against the sheath surrounding it, irritating the sheath and causing it too to become inflamed and swollen. It has a poor blood supply, which can make it susceptible to injury and can make recovery from injury slow. Factors that can lead to the development of Achilles tendonitis include, tight or weak calf muscles, rapidly increasing the amount or intensity of exercise. Hill climbing or stair climbing exercises. Changes in footwear, particularly changing from wearing high-heeled shoes to wearing flat shoes. Wearing inadequate or inappropriate shoes for the sporting activity being undertaken. Not adequately warming up and stretching prior to exercise. A sudden sharp movement that causes the calf muscles to contract and the stress on the Achilles tendon to be increased. This can cause the tendon fibres to tear.
Symptoms
The Achilles tendon is a strong muscle and is not usually damaged by one specific injury. Tendinitis develops from repetitive stress, sudden increase or intensity of exercise activity, tight calf muscles, or a bone spur that rubs against the tendon. Common signs and symptoms of Achilles Tendinitis include, gradual onset of pain at the back of the ankle which may develop in several days up to several months to become bothersome. Heel pain during physical activities which may diminish after warming up in early stages, or become a constant problem if the problem becomes chronic. Stiffness at the back of the ankle in the morning. During inactivity, pain eases. Swelling or thickening of the Achilles tendon. Painful sensation if the Achilles tendon is palpated. If a pop is heard suddenly, then there is an increased chance that the Achilles tendon has been torn and immediate medical attention is needed.
Diagnosis
To diagnose the condition correctly, your doctor will ask you a few questions about the pain and swelling in your heel. You may be asked to stand on the balls of your feet while your doctor observes your range of motion and flexibility. The doctor may also touch the area directly. This allows him to pinpoint where the pain and swelling is most severe.
Nonsurgical Treatment
The aim, when treating Achilles tendinitis, is to relieve pain and reduce swelling. The kind of treatment used can vary, based on the severity of the condition and whether or not the patient is a professional athlete. After diagnosis, the doctor will decide which method of treatment is required for the patient to undergo, it is likely that they will suggest a combination. Stretching achilles tendon, a doctor might show the patient some stretching exercises that help the Achilles tendon heal, as well as preventing future injury. Methods used to treat Achilles tendinitis include, ice packs - applying these to the tendon, when in pain or after exercising, can alleviate the pain and inflammation. Resting, this gives the tissue time to heal. The type of rest needed depends on the severity of the symptoms. In mild cases of Achilles tendinitis, it may mean just reducing the intensity of a workout, in severe cases it might mean complete rest for days or weeks. Elevating the foot, swelling can be reduced if the foot is kept raised above the level of the heart. Exercise and stretching, a doctor might show the patient some stretching exercises that help the Achilles tendon heal, as well as preventing future injury. They may, instead, refer the patient to a physiotherapist or another specialist. The exercises learned will improve the flexibility of the area and likely increase calf strength. Pain relievers - non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS), such as ibuprofen can reduce pain and swelling. If you suffer from asthma, kidney disease or liver disease do not take NSAIDs without first checking with your doctor. Steroid injections, these can reduce tendon swelling, but should be performed with caution, as this process has been associated with a greater risk of tendon rupture. A doctor would likely perform the injection while scanning the area with ultrasound to reduce this risk. Compression bandages and orthotic devices, such as ankle supports and shoe inserts can aid recovery as they take the stress off the Achilles tendon.

Surgical Treatment
Most people will improve with simple measures or physiotherapy. A small number continue to have major problems which interfere with their lifestyle. In this situation an operation may be considered. If an operation is being considered, the surgeon will interview you and examine you again and may want you to have further treatment before making a decision about an operation. Before undergoing Achilles tendonitis surgery, London based patients, and those who can travel, will be advised to undergo a scan, which will reveal whether there is a problem in the tendon which can be corrected by surgery. Patients will also have the opportunity to ask any questions and raise any concerns that they may have, so that they can proceed with the treatment with peace of mind.
Prevention
The following measures can significantly reduce the risk of developing Achilles tendonitis. Adequately stretch and warm up prior to exercise. Warm down and stretch after exercise. Choose footwear carefully and use footwear appropriate to the sport being undertaken. Use orthotic devices in footwear to correctly support the foot. Exercise within fitness levels and follow a sensible exercise programme. Develop strong, flexible calf muscles.